Edit package
Overview
Edit is the subpackage located under packages/edit exposing Vue 3 components. It is used by the Content Element authors to create a Content Element. It consists of three main components:
- Edit component; main authoring component, required
- Top Toolbar component; exposing Content Element controls within the Tailor CMS top toolbar slot; optional
- Side Toolbar component; exposing Content Element controls within the Tailor CMS side toolbar slot; optional
In the example image below, you can see a WYSIWYG editor Edit component (displaying 'Edit component' text) and its Top Toolbar; exposing various editor controls (mounted below the main application heading). Side Toolbar is not exposed for this Content Element; in case if it was, it would be visible upon element selection instead of Browse sidebar (note that element tab in the bottom left corner is greyed out).
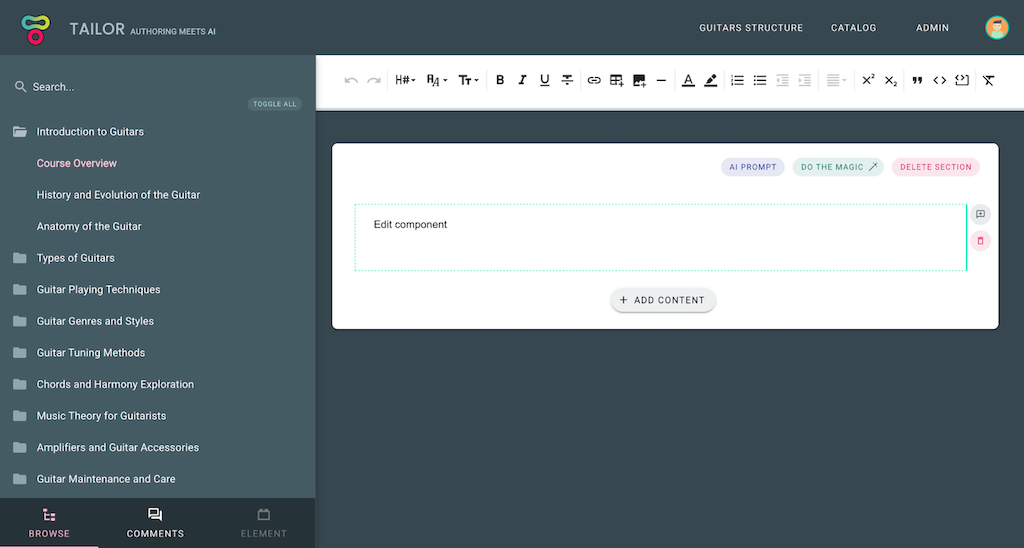
These are regular Vue components which are being passed element related props:
:element: object; Element entity containing all element related data:isFocused: boolean; Is element selected:isDragged: boolean; Is element being dragged; e.g. upon reordering:isReadonly: boolean; Should element be readonly; e.g. upon copy element seleciton
and observed for element related events:
@save- Emitdataobject to be saved on theelement.dataproperty.@delete- Delete element (default control already exists)
As noted above, to store element state, simply emit save event passing an object to store (which will be persisted on the element.data property). To set the initial state of the element.data property, you need to define the initState function. The initState function generates the initial element.data value. For more details on how to do that, please visit the State section.
Here is an example of a simple counter Edit component from the Introduction section:
Edit.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>Times clicked: {{ element.data.count }}</div>
<button @click="increment">Increment</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { Element } from 'tce-manifest';
const props = defineProps<{ element: Element }>();
const emit = defineEmits(['save']);
const increment = () => {
const { data } = props.element;
const count = data.count + 1;
emit('save', { ...data, count });
};
</script>
In the example above, component triggers save state event on each Increment button click. Note how data object is recreated, rather than count value being modified. Since data flow should be top-down it is important not to modify the recieved value, but rather emit a new state (to avoid side-effects). After the event has been triggered, change is recieved via prop (updated element state). Similar goes for the TopToolbar:
TopToolbar.vue
<template>
<button @click="decrement">Decrement</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { Element } from 'tce-manifest';
const props = defineProps<{ element: Element }>();
const emit = defineEmits(['save']);
const decrement = () => {
const { data } = props.element;
const count = data.count - 1;
emit('save', { ...data, count });
};
</script>Communication between components
Info
Available in version >=0.1.0
All authoring components have the $elementBus pub/sub mechanism available, provided via Vue provide/inject prop-drilling feature. To communicate between components, simply inject $elementBus and emit the event.
TopToolbar.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
...
const elementBus = inject('$elementBus');
const decrement = () => {
// Emit decrement event upon toolbar btn click
elementBus.emit('decrement', { count });
};
...
</script>
Proceed by implementing a listener within the targeted component (using the on registration method):
Edit.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
...
const elementBus = inject('$elementBus');
elementBus.on('decrement', ({ count }) => console.log(count));
...
</script>For more details on the entire pub/sub API see the vue-radio implementation.
When to save the state ?
Depending on the type of the element, you might wonder what is the best moment to persist element state. Most of the elements are observing isFocused prop and triggering save state event upon user focusing out of the element. Of course, this is not always possible, e.g. when element input needs to be validated. In those cases we suggest explicit save button.
Readonly state
Each Content Element needs to implement the readonly behaviour which is activated when isReadonly prop is set to true. Readonly element presentation is used for various features like observing Content Element diff or for copy functionality (Content Element needs to be previewed in order to be selected).
Composite Elements
Content elements can be configured as composite elements using the isComposite flag in the manifest. To include a list of composite elements, utilize the TailorEmbeddedContainer global component. Tailor CMS will render the appropriate element list, while the CEK runtime will mock example elements.
The TailorEmbeddedContainer component accepts the following props:
:container: object; Data field of the element containingembedsin a key-value format.:allowed-elements-config: array; Array of element configs allowed to be embedded. Usually equals to theembedElementConfigprop passed to the Edit package.:isReadonly: boolean; Indicates if the element should be readonly. Defaults tofalse.:enableAdd: boolean; Indicates if adding new elements is allowed. Defaults totrue.:addElementOptions: object; Additional options passed to the AddElement core component.
Question Elements
Content elements can be configured as question elements using the isQuestion flag in the manifest. Each question can utilize QuestionContainer component from @tailor-cms/core-components package which is used to wrap the component in the container with the question prompt, content element slot, hint, optionally feedback and save and cancel actions. If QuestionContainer is used content element must also be configured as isComposite in the manifest because Question prompt is utilizing TailorEmbeddedContainer under the hood.
The QuestionContainer component accepts the following props:
:elementData: object; Element entity containing all element related data:showFeedback: boolean; Controls whether QustionContainer should render feedback component.:embedElementConfig: array; array of element configs allowed for the Question prompt:isReadonly: boolean; Should element be readonly; e.g. upon copy element seleciton